A sharp increase in viral infections. Pathogens attack one organ in particular

Recently, the number of viral infections has increased significantly in Poland. They mainly affect the digestive tract. See what symptoms to look out for and what to do to avoid infection.
Every year, the Department of Infectious Disease Epidemiology and Surveillance of the National Institute of Health publishes a report on the incidence of selected infectious diseases. The data from the latest report are quite disturbing. It turns out that the number of patients with viral infections has increased significantly recently. Symptoms develop in a relatively short time, especially in one organ. See what signals should concern you.
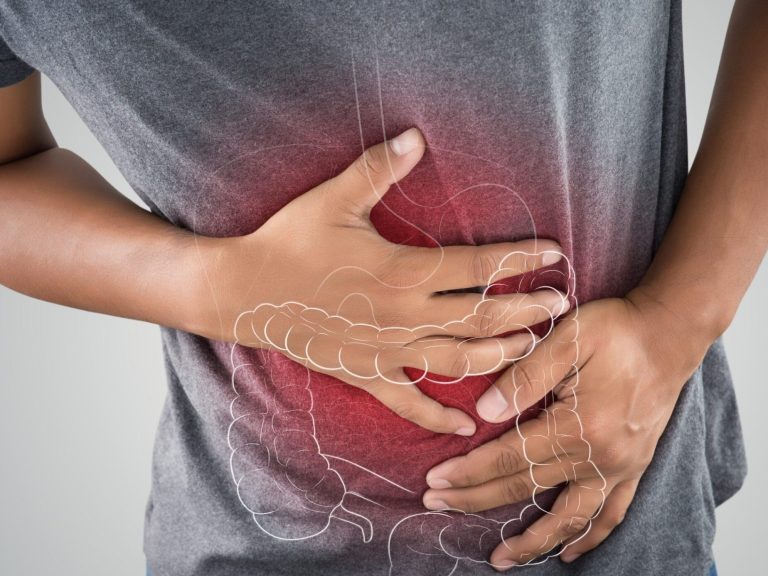
Viral infections attack the intestines
The Division of Infectious Disease Epidemiology and Surveillance of the National Institute of Health recorded significant increase in viral intestinal infections. In the period between January 1 and April 30, 2024, 13,523 cases were reported. For comparison, in the same period last year their number was only 7,562. Almost twice as many infections were observed among young children up to two years of age. The disease is caused by, among others, rotaviruses and noroviruses, and not, as is commonly believed, the influenza virus. However, viral intestinal infections are commonly referred to as stomach flu. Another name often used is enteritis.
What symptoms do viral intestinal infections cause?
Viral intestinal infections cause many different digestive symptoms. They can easily be confused with food poisoning. Patients usually complain of abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. The most frequently reported symptoms also include: watery diarrhea, dizziness and fatigue. The first disturbing signals from the body can be noticed just a few hours after infection.
It is worth emphasizing that viral intestinal infections are highly contagious. One family member can quickly infect other household members. Pathogens are transmitted through food or droplets. Infection may also occur through contact with an infected person and everyday objects. Generally, the infection is mild and its symptoms disappear quickly. However, it may turn out to be very dangerous. This especially applies to children, seniors and people with weakened immune systems.
How to reduce the risk of viral intestinal infections?
First of all, you should ensure that you follow the rules of personal hygiene. It is worth washing your hands often and avoiding large crowds. If you notice symptoms of infection, stay at home and limit contact with other people. Remember to drink plenty of fluids. If the symptoms do not subside after a few days, see your primary care physician.