Loneliness also affects our body. Scientists have investigated what diseases it can lead to

Suffering is not the only consequence of loneliness. In lonely people, the body is constantly stimulated, which in turn is a serious risk factor for a specific group of diseases.
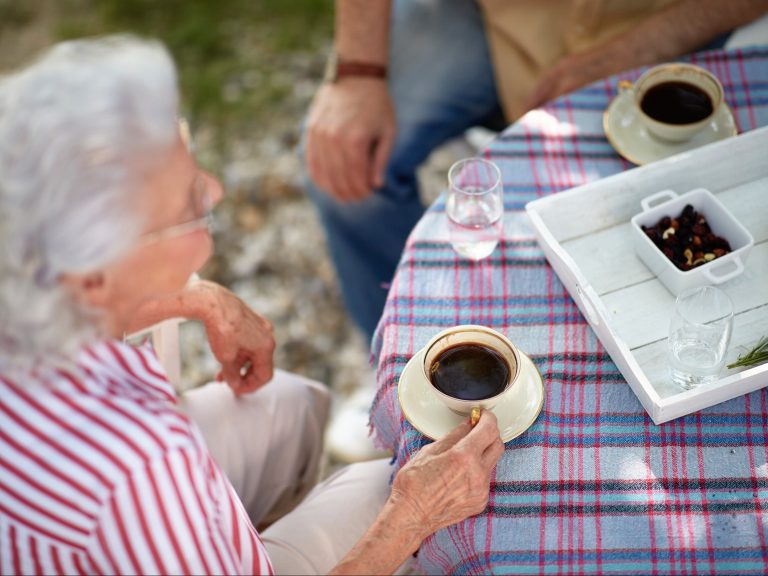
Although loneliness is not a disease, this condition may contribute to the development of certain diseases. It’s not just about depression, it can also have a specific impact on the physical condition of our body. However, it should be remembered that loneliness is very subjective and we can experience this state even when we are among people. There is no specific pattern to how people experience loneliness – external factors, such as lockdown, can cause the condition, but are never a single culprit. However, it is worth remembering that it is completely natural that every person feels lonely from time to time, but the key is how we deal with this condition. It is also known that loneliness can cause more harm than smoking 15 cigarettes a day. Recent research also shows that lonely people have trouble distinguishing real people from fictional characters.
Loneliness and diseases – research
Dr. Łukasz Okruszek from the Institute of Psychology of the Polish Academy of Sciences checked how loneliness affects human physiology. The scientist got the idea for the study from social psychology. However, he examined an aspect that this field of psychology does not address, namely the impact of loneliness on the human body. It turns out that loneliness, apart from affecting our psyche, can also lead to cardiovascular diseases.
The scientist and his team “induced” artificial loneliness in the test subjects in laboratory conditions. The study was conducted on 129 people. In this way, the researchers checked how physiological conditions change in a person who is in this state. “After the respondents completed questionnaires measuring, among other things, personality traits, we provided a randomly selected group of participants with information that based on the results obtained, we could conclude that they would be lonely in the future. We then checked how such information affected the parameters measured in the ECG and brain activity,” said Dr. Łukasz Okruszek in an interview with PAP.
How does loneliness affect the human body?
Loneliness is a specific type of stressor – it increases the resistance of the body’s systems that are supposed to protect it against the negative effects it leads to. “In response to the stimulus – the thought of loneliness awaiting us in the future, the activity of the immune and sympathetic systems increases – so we can say that our body is in a state of increased activation and readiness to ‘defense’. However, the reaction of the parasympathetic system, which balances their work, decreases, and after a period of mobilization in a healthy functioning body, it allows us to rest,” the scientist explained.
In people who are lonely, the body is constantly stimulated, and the parasympathetic system does not compensate for this reaction. Consequently, this may lead to reduced heart rate variability, which is associated with a lower parasympathetic response. Researchers have already observed this in people in whom they induced feelings of loneliness only for a short period of time.
“Chronic loneliness and long-term lack of contact with other people exist a serious risk factor, including for cardiovascular diseases. This should also be knowledge promoted at the level of primary care physicians. The internist should ask about the patient’s mental well-being. Isn’t it strange that many people know what their blood pressure and cholesterol levels are – but do not take into account the impact of loneliness or social isolation on their health? This can be a source of suffering that may lead to specific diseases,” concluded Dr. Łukasz Okruszek.