Hoarseness is an inconspicuous but dangerous symptom. May herald “silent reflux”
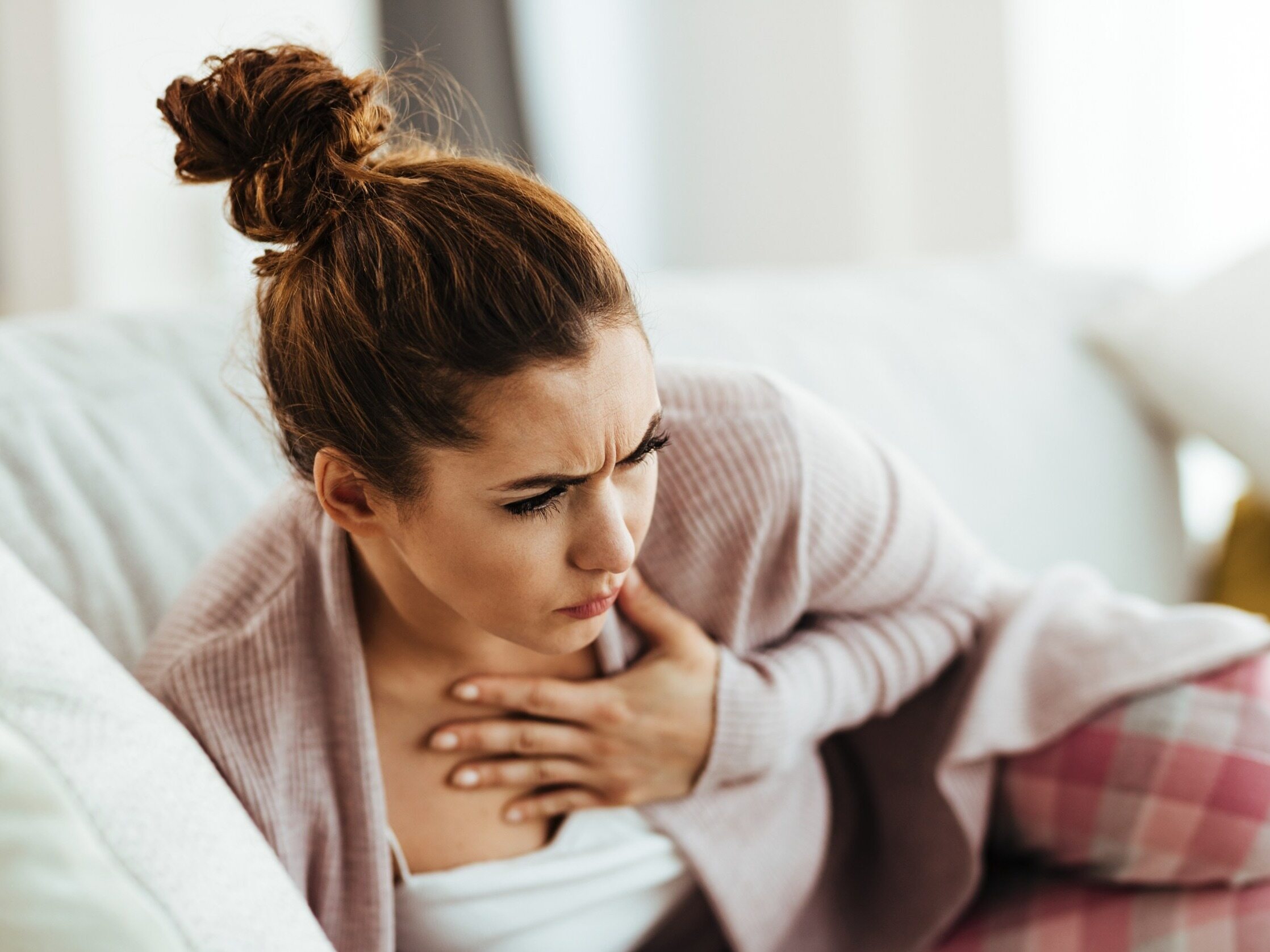

Hoarseness is often underestimated. We usually put it down to a cold, talking too long, or throat irritation. Meanwhile, the cause of the problem often lies elsewhere. This symptom may be a harbinger of many serious diseases. One of them is the so-called silent reflux.
“Silent reflux” is laryngopharyngeal reflux. It gained the indicated “nickname” because it is difficult to diagnose. It is not as common as GERD, or gastroesophageal reflux disease. However, this does not mean that it should be ignored. It can lead to many serious complications, for example chronic pneumonia or damage to the vocal cords. In people with this disease, stomach contents flow back through the esophagus into the larynx and pharynx and irritate the epithelium of the upper respiratory tract.
How does “silent reflux” manifest itself?
Laryngopharyngeal reflux causes ambiguous symptoms that may indicate many different diseases. That is why it is so difficult to make the correct diagnosis. What symptoms are worth paying special attention to? Not only should you be concerned about hoarseness, but also:
-
cough,
-
persistent throat clearing,
-
burning in the throat,
-
mucus in the upper respiratory tract,
-
unpleasant taste in the mouth after waking up,
-
difficulty swallowing
-
short, uncontrolled contractions of the vocal cords or larynx.
The last of the mentioned signs seems to be the most terrifying. Professor of otolaryngology Claudio Milstein of the Cleveland Clinic points out that patients experiencing this symptom cannot breathe. It usually lasts a few seconds, but for sufferers this moment seems like an eternity and causes panic attacks.
What is the diagnosis of “silent reflux”?
Gastroenterologists and laryngologists usually diagnose the disease based on a medical interview and an in-depth analysis of the symptoms reported by the patient. They also often order laryngoscopy. This examination allows for the assessment of the condition of the throat, larynx and vocal cords. Thanks to it, the doctor is able to check whether there are any pathological changes in the indicated area, for example tumors or polyps. The diagnosis may also be made easier by measuring the amount of pepsin in the patient’s saliva. It’s a digestive enzyme. Its presence in the mouth indicates that the contents of the stomach are refluxing into the esophagus. However, this type of examination is not performed very often when laryngopharyngeal reflux is suspected.
Treatment of laryngopharyngeal reflux
“Silent reflux” therapy primarily involves administering proton pump inhibitors to the patient. These are preparations that inhibit the secretion of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. They are also used to treat GERD.
The success of the therapeutic process depends largely not only on taking appropriate preparations. Modifying your lifestyle and eating habits is also important. Doctors recommend that:
-
give up eating very spicy foods,
-
quit tobacco and vaping addiction,
-
eat your last meal no later than three hours before bedtime,
-
increase physical activity and lose excess weight.
Sometimes it is also advisable to start speech therapy (in case of major voice problems).
What else can hoarseness indicate?
Hoarseness often accompanies laryngeal diseases. It may also indicate the presence of so-called singing nodules, i.e. growths on the vocal folds. This problem mainly concerns people for whom the voice is a working tool (teachers, actors, lectors, vocalists, etc.). Hoarseness may also be a symptom of throat, larynx or lung cancer.
If you notice hoarseness that does not go away on its own after taking appropriate measures (for example, moisturizing the throat) and lasts longer than a few hours or days, contact your primary care physician and ask for a referral to an ENT specialist. You can also visit a specialist privately. There is a fee for such a visit. Its cost usually ranges from PLN 80 to PLN 300 (depending on the city and the reputation of the office).